Swarts Reaction is an organic reaction that converts alkyl chlorides/alkyl bromides to alkyl fluorides. Frederick Jean Edmond Swarts reported this method in 1892.This reaction is carried out by heating the alkyl chloride/alkyl bromide in the presence of heavy metal fluorides such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2, or SbF3.
Swarts fluorination is another name for the swarts reaction.
Interesting Science Videos
What is Swarts Reaction?
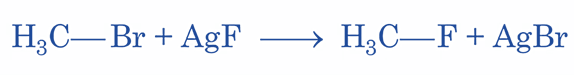
Swarts reaction (also known as halogen exchange reaction or swarts fluorination reaction) is a procedure that converts alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide to alkyl fluoride. This is accomplished by heating the alkyl chloride/bromide in the presence of a heavy metal fluoride (for example, silver fluoride or mercurous fluoride). If sodium fluoride or potassium fluoride are employed, the reaction will occur, but the yield will be much reduced.
It is the most effective method for producing alkyl fluorides. To activate this reaction, we can heat alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide in the presence of heavy metal fluorides.
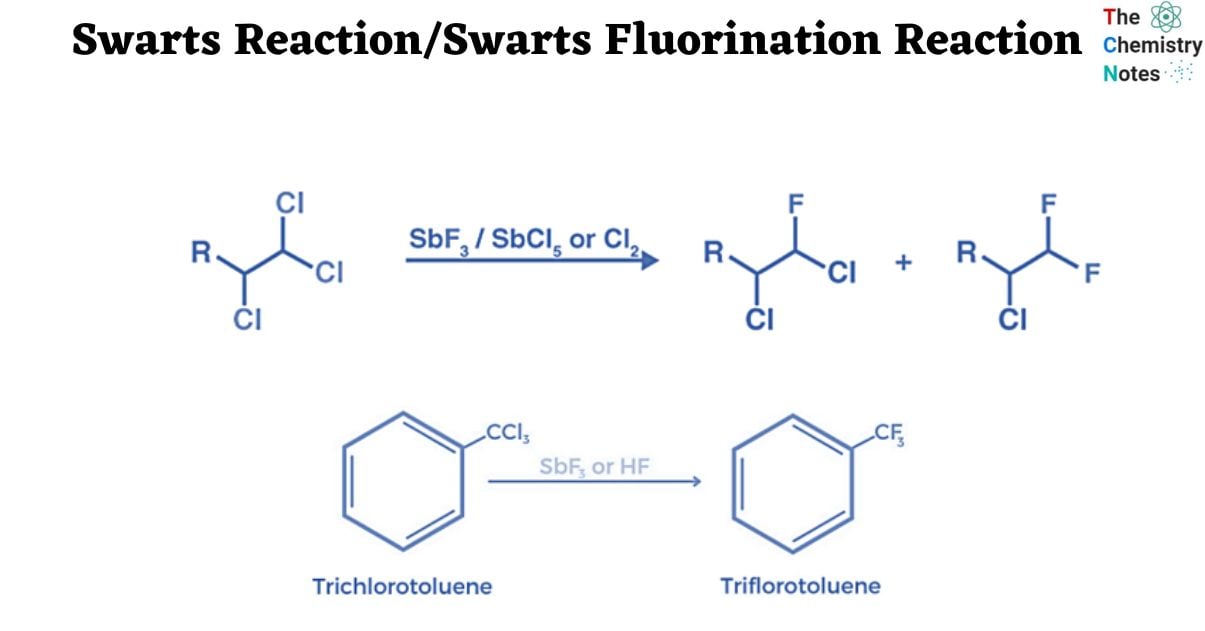
The Swarts reaction can be understood using the following example:
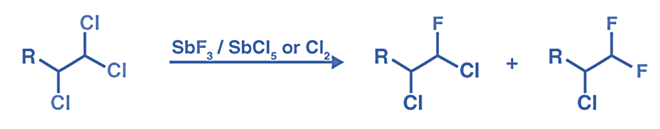
The Swarts Reaction Mechanism
- The Swarts reaction occurs via the SN2 reaction.
- The metal-fluorine link is broken, and a new bond is formed between carbon and fluorine. The displaced chlorine or bromine atoms form a connection with the metal.
- The Swarts fluorination reaction mechanism is based on the concept of greater electronegative components replacing lower electronegative elements.
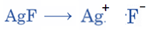
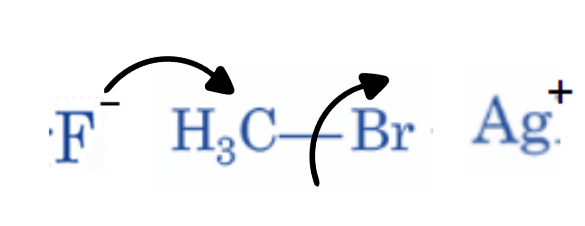
Swarts rule states that the fluoride formed during fluorination frequently has a lower boiling point than the comparable chloride.
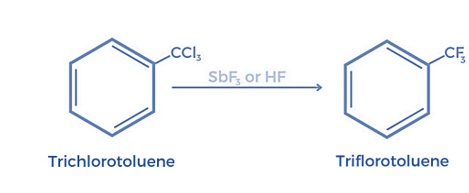
Furthermore, chlorinated hydrocarbons can be reacted with metallic fluorides to form fluorinated hydrocarbons. As a result, Swarts fluorination can be used to totally replace chlorine or bromine with fluorine in alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides.
Application of Swarts Reaction
- Alkyl fluorides are created through this process.
- Fluorinated aliphatic organic molecules, or Freons, are produced via a different variation of the same process. (Freons are fluorinated aliphatic organic molecules.)
- Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is fluorinated to produce Freons in the presence of antimony salts, which exhibit the oxidation states +3 and +5.
Limitations of Swarts Reaction
- The reaction may not be suitable enough for tertiary and secondary halides.
- The potentiality of formation of side products.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
Is Swarts Reaction SN2?
Swarts fluorination reaction involves the breaking of a metal-fluorine bond and the creation of a carbon-fluorine link. As a result, one halogen atom gets replaced by another. Swarts reaction is thus an SN2 reaction.
What is Swarts reaction explain with example?
Swarts fluorination reaction is commonly used to separate alkyl fluorides from alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides. This is achieved by heating the alkyl chloride / bromide in the presence of fluoride in certain heavy metals.
Which reagent is used in the Swarts reaction?
The combination of antimony trifluoride and chlorine (SbF3 + Cl2) is known as the Swarts reagent.
Why is AgF used in Swarts Fluorination Reaction?
In this reaction, higher alkyl halides (R-Cl) react with lower metal halides (AgF) to produce lower alkyl halides (R-F). If heavy metal fluoride is not used, F ion cannot displace Cl/Br. The reaction will either fail or result in the production of a new chemical.
References
- Morrison R. T. & Boyd R. N. (1983). Organic chemistry (4th ed.). Allyn and Bacon.
- Smith M. & March J. (2001). March’s advanced organic chemistry: reactions mechanisms and Structure (5th ed.). Wiley.
- Ghosh, S.K., Advanced General Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, New Central Book Agency Pvt. Ltd., Kolkatta, 2007.
- Bahl, B.S., A., Advanced Organic Chemistry, S. Chand and Company Ltd, New Delhi, 1992.
- https://protonstalk.com/haloalkanes-and-haloarenes/swarts-reaction/
- https://collegedunia.com/exams/swarts-reaction-mechanism-applications-and-sample-questions-chemistry-articleid-6345
- https://testbook.com/chemistry/swarts-reaction
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/swarts-reaction/#
