It’s necessary to become familiar with laboratory equipment when working in different labs. Chemistry labs conduct experiments to ascertain the chemical characteristics of various elements and compounds. Both general-purpose and specialized equipment may be needed for the chemical lab. A bunsen burner, crucible, weighing scale, litmus paper, and glassware such as test tubes, beakers, and funnels are among the general-purpose tools used in the chemistry lab.
Since the first day of basic chemical experimentation in school laboratories, students should have a comprehensive understanding of the appropriate and essential chemistry lab apparatus. It is important that students have a solid understanding of the various equipment, and educational institutions must take extra effort to ensure that students are aware of this.

Let us have a brief knowledge about some common apparatus used in chemistry lab.
Interesting Science Videos
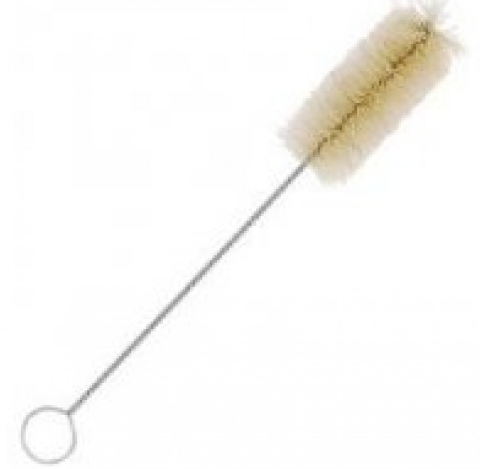
Brushes
Laboratory brushes serve as fine hand instruments used in laboratories, made for a range of cleaning tasks. Test tubes, beakers, burettes, cylinders, centrifuges, flasks, and burettes may all be cleaned using specialized brushes. There are other cleaning applications for which these lab brushes are beneficial. These consist of deburring, polishing, rust removal, pre-soldering, and chemical etching erasing.

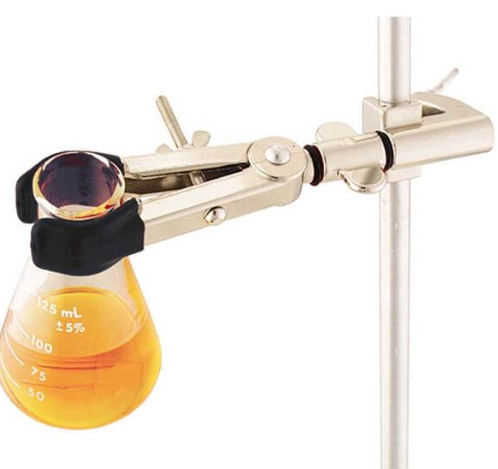
Burette Clamp
A burette clamp is a laboratory instrument that is used to secure a burette during titration or other scientific processes that require accurate volume measurement. The clamp has two jaws that may be tightened around a burette’s neck. The jaws are often constructed of plastic or metal. The jaws are fixed to a height-and position-adjustable stand or rod to suit various experimental configurations.
In labs dealing with chemistry, biology, and medicine, where precise liquid measurement and dispensing are crucial, the burette clamp is frequently utilized. It keeps a burette stable and erect so that it doesn’t slide or fall while the titration is being done. The burette’s height may also be changed using the clamp. In addition, the clamp may be utilized to guarantee precise measurement, regulate liquid flow, and raise or lower the burette.
To guarantee efficiency and safety when using a burette clamp, it must be handled carefully.
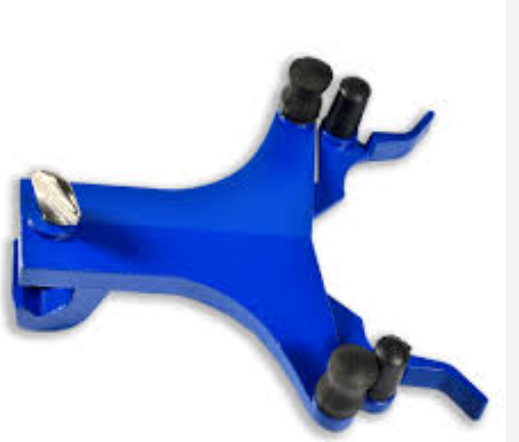

Clamps
A sturdy support or frame must always be attached to laboratory equipment, such as vacuum lines, Soxhlet extractors, distillation setups, and the like. There exists a vast array of distinct types of clamps. When using general-purpose clamps to secure glassware, make sure that the inner surfaces of the “jaws” and “fingers” of the clamp are covered with rubber or cork to act as a cushion for the glass. This will prevent metal from coming into contact with the glass in the unlikely event that the clamp is overtightened and the glass is crushed. Clamping conical flasks at the neck and ground-glass jointware at the joint, which typically has the thickest glass, are the proper clamping techniques.

Cork
A cork is a tiny, cylindrical stopper composed of cork oak tree bark. Corks are used in laboratories to seal glassware, including bottles, flasks, and test tubes. They are available in different sizes, and their selection is usually determined by the size of the aperture in the container they are going to close. Corks can also be shaped or trimmed to fit a particular container.

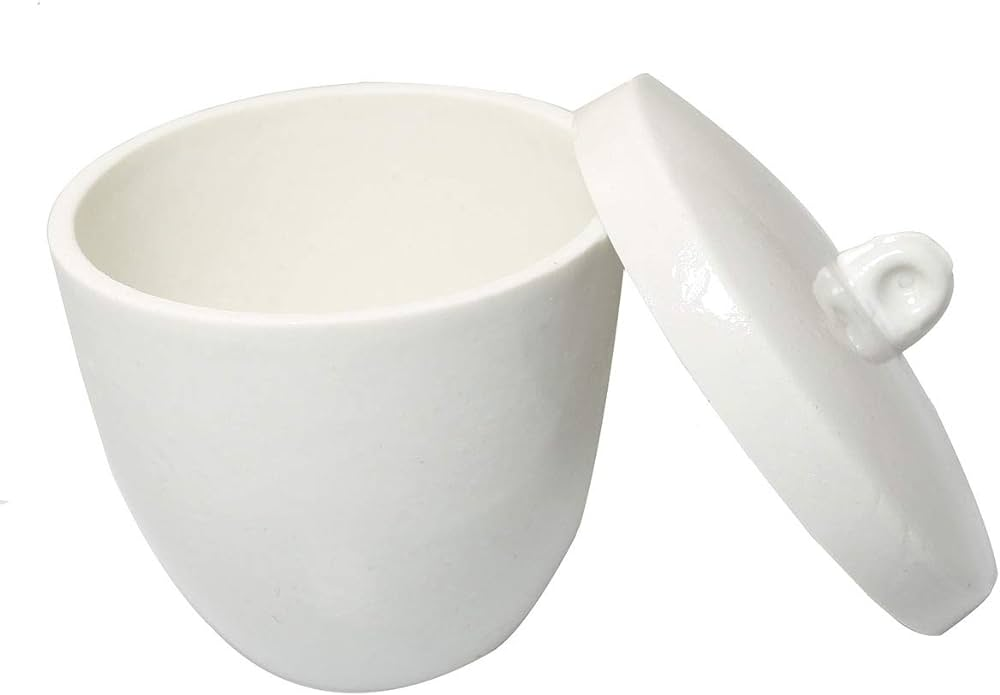
Crucibles
A form of glassware used in laboratories called crucibles is used to combine, melt, and burn solid chemical substances over a burner. It is capable of holding a wide range of materials, fluids, and chemicals. It is also applied in chemical analysis that is quantitatively gravimetric. Crucibles are great for laboratory studies requiring extremely hot chemical reactions, as well as corrosive and coloring processes, because of their capacity to resist extremely high temperatures. It is a typical piece of equipment in chemical labs used for studies using heat. Crucible’s significance is further highlighted by the fact that it improves a lab technician’s efficiency and efficacy.

Droppers
Droppers are tools for transferring and measuring tiny volumes of liquids. They are made up of a long rubber bulb at the top and a long plastic or glass tube with an aperture at the end. This rubber bulb may be squeezed to release the necessary liquid. When we needs to transfer small amount of chemicals in lab we use droppers so that we get efficient results.
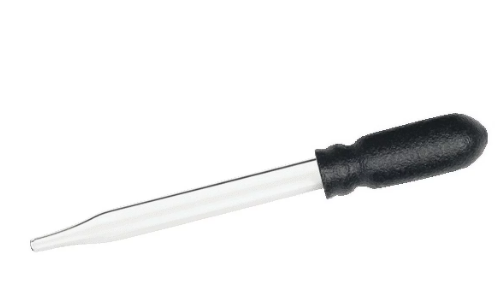
Evaporating Dish
A porcelain laboratory dish used for liquid evaporation is called an evaporating dish. It is often employed in chemistry and other scientific fields for a number of tasks, including crystallizing compounds, concentrating solutions, and extracting dissolved materials from solutions by evaporating the solvent. These dishes are appropriate for handling corrosive materials, acids, and bases since they often exhibit resistance to a broad variety of chemicals. There is less chance of spills while using evaporating dishes because of their elevated walls and flat bottom. Because of its shallow, flat shape, the contents can be heated evenly, resulting in consistent evaporation or crystallization.

Filter Papers
Lab filter sheets are quite effective in absorbing liquids. The solution and the solid can be separated in this way. The filtering procedure can be carried out at a slow, medium, or rapid speed, depending on the kind of paper that is utilized. Filter sheets are typically directed. The fibres on the front side are looser, but the fibres on the back side, the mesh surface, are tighter.
Lab filter sheets come in two varieties: qualitative and quantitative. The name “qualitative filter paper” comes from its application in qualitative analysis. The application includes a separation method for determining and identifying items. When filtered using this kind of filter paper, more cotton fibers are produced. It has a high wet strength, which allows it to endure pressure and vacuum filtration. Quantitative and gravimetric measurements are made using quantitative filter sheets. Additionally, the filter paper prevents the paper from reacting with common substances. Because of this, it generates less contaminants, which makes it perfect for quantitative work.

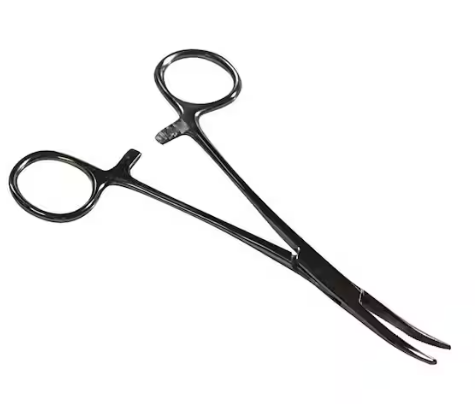
Forceps
Laboratory forceps are tiny instruments meant to pick up things too small for the human fingers to handle with ease. They are available in a variety of forms and sizes; they can be shiny and fresh, worn and discolored, sharp and pointed, or flat-ended. Different types of forceps exist, such as the thumb, locking, and Kelly forceps.
Chemistry labs can benefit from the use of tweezers or thumb forceps. Forceps are used in chemistry labs for holding substances like sodium metal and other chemicals and solids that shouldn’t be handled with bare hands.

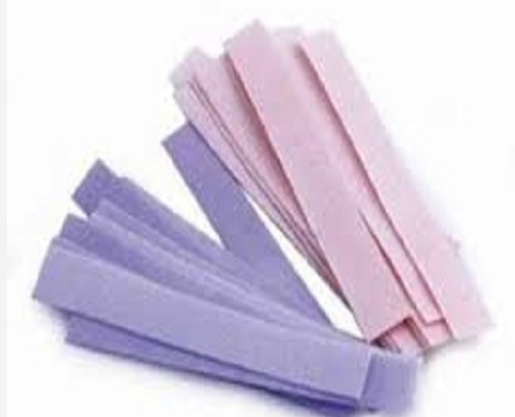
Litmus Paper
Litmus paper is a type of filter paper that has been naturally dissolved dyed by lichen. Litmus paper is a type of paper that provides a result that may be used as a pH indicator.
Litmus paper or pH strips are used to measure the acidity and alkalinity of a solution. While pH strips measure the solution’s pH, litmus paper assesses the solution’s acidity and alkalinity. When the solution is basic or alkaline, litmus paper turns blue; when the solution is acidic, it turns red.

Magnetic Stir Bar
Magnetic stir bars are magnets that have been coated and are used to mix liquids in a closed container. They don’t need a container opening in order to mix liquids. They are a common method for agitating liquids in smaller containers. Magnetic stirrers have application in biology and chemical research, particularly in the medical field. This setup’s main benefit is that you may swirl the liquid without worrying about anything sticking to the container. It is possible to seal the container entirely. Lubricants cannot contaminate the fluid and there is no risk of leakage when there is no spinning shaft protruding into the container.
Mortar and Pestle
The Mortar and Pestle is an example of a piece of equipment that has a set of paired instruments as well as a bowl-cup construction with a rod.
These two laboratory tools are used to help grind and crush materials. The mortar resembles a bowl in form. It is made of long-lasting materials such as ceramic or stones. Cast from the same material as mortar, the pestle is a club-shaped piece of grinding equipment. In daily life, a mortar and pestle are useful tools for grinding different grains and other ingredients. They are employed in chemical labs for the purpose of breaking down large solid particles to tiny sizes.

Pipet Bulbs
To manually fill serological or volumetric pipettes instead of using a mouth suction, a pipette bulb serves as a source of pressure or vacuum. It is constructed of natural rubber. The use of a pipette bulb removes the necessity for handling hazardous chemicals and risky mouth pipetting.

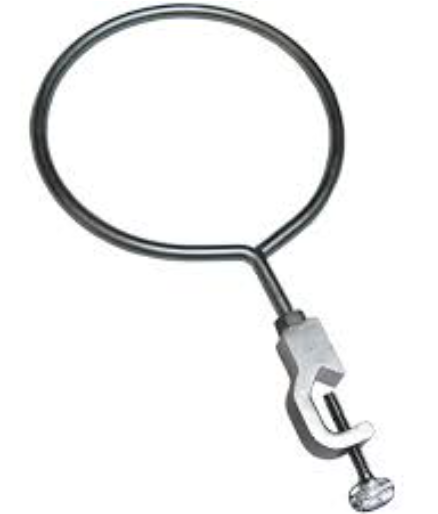
Rings
An iron ring, also known as a ring clamp, is a laboratory device made out of a metal ring-like loop that is used to hold different scientific equipment that cannot be put on flat surfaces, such as funnels, Imhoff cones, and occasionally even round-bottom flasks. In some situations, the rod ends in a screw clamp that may be fastened to a retort stand or other support; in others, the rod can be mounted to a stand using a laboratory clamp holder. In chemical laboratories, iron rings are widely employed to support apparatus above the work surface.

Scoopulas
Scoopulas are long, scoop-shaped metal objects. They are used interchangeably with spatulas to transfer solids: to a weigh paper for weighing, to a coverslip for melting point, to a watch glass for scraping, and so on. Because they can retain more solid than spatulas, they are frequently the best choice for transferring bigger amounts of chemicals.
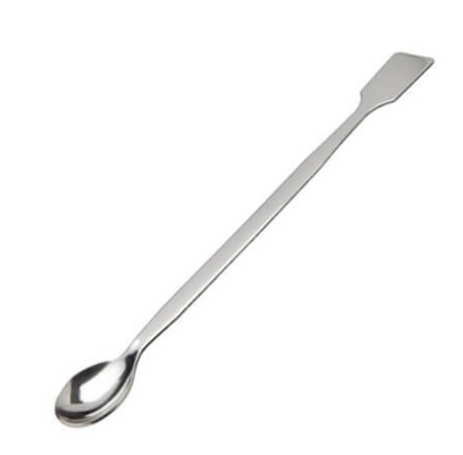
Spatulas
A spatula is a laboratory tool with one or two spoon-like scoops or flat ends that is widely used for transferring chemical reagents or other materials. Spatulas are often constructed of metal, typically stainless steel, but plastic, glass, or glazed ceramic spatulas are also available. To avoid contaminating the chemicals, simple steel spatulas are normally avoided.
Metal spatulas are resistant to the majority of chemical reactions, however they are not compatible with strong acids, certain salts (such as copper salts), or halogens (iodine). It is not recommended to leave them on an open flame for too long since they may colorize.
Metal and plastic spatulas are frequently preferred over glass or glazed ceramic spatulas because they are not fragile and will not shatter if dropped on the floor (a regular occurrence in laboratories). Wood spatulas should only be used with dry, non-corrosive chemicals that are insoluble in most solvents. They are occasionally employed while working with energetic materials.

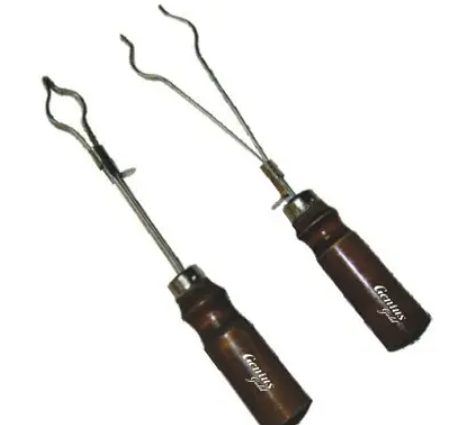
Test Tube Holders
A test tube holder is an apparatus that holds test tubes. It’s used to keep a test tube in place when it’s hot or shouldn’t be handled. Furthermore, when heating the tube with liquid or solid contained within, the holder should securely grasp the test tube in order for the tube to be held safely during heating.

Tripod Stand
A tripod stand is a laboratory piece of equipment used to hold a beaker, flask, or other container during heating. The stand is made up of three legs joined at the top by a ring or clamp. A Bunsen burner or other heat source is put beneath the container, and the container is placed on top of the ring or clamp. The tripod stand gives the container a sturdy basis and helps to prevent spills or mishaps during heating. It also enables for simple adjustment of the container’s height above the heat source. Overall, the tripod stand is an important piece of equipment in many laboratory settings, notably in chemistry and biology labs where liquid heating is widespread.

Thermometers
Laboratory thermometers have a high level of precision and are used for applications such as experiment monitoring, instrument calibration, materials testing, and maintaining a sterile work environment. The operation of a laboratory thermometer is determined by its kind. They are usually a liquid-in-glass device, a bimetallic strip, an electronic thermistor thermometer, or an infrared (IR) device. All of these thermometers display temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Depending on the sort of laboratory investigation, they can be employed in a variety of applications.

Tongs
Tongs are a useful tool for gripping and lifting items instead of holding them in your hands. They come in different forms and with different numbers of prongs for different uses, such as grasping flasks, beakers, and crucibles.
Lab tongs are often constructed to suit certain objects, with long handles to keep the user a safe distance away from an object that is hot or otherwise dangerous to grasp. Beaker tongs’ arms are designed to assist grasp beakers of varied sizes. Some beaker tong arms are plastic-coated to decrease slippage and prevent heating of the metal tongs. Typically used to hold hot beakers, the jaws’ ends may also be wrapped or coated with an insulating substance.

Vials
Vials are glass containers with flat bottoms and either screw-on caps or stoppers. They are available in a variety of sizes and forms and are intended to contain little volumes of liquids or solids. vials are used for general sample collection, storage, and transportation; available in a range of colors, sizes, volume capacities, and material compositions; may be sterile, non-sterile, and/or autoclavable; caps may be included.
The name “vial” is rather ambiguous, although it is typically defined as a tiny, cylindrical, flat-bottomed container used to carry liquids. The majority of sample vials are composed of plastic or glass, with a separate or connected cover or seal. Sample vials are classified according to their material, size, and purpose. Glass sample vials are classified according on the type of glass used to produce them.
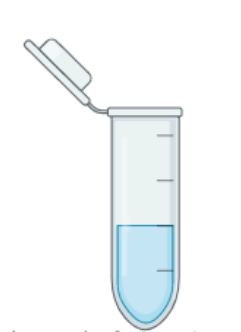
Wash Bottles
While wash bottles are mostly used in laboratories to wash or rinse various types of glassware or plasticware, they also have less common applications such as correctly filling volumetric flasks.
Wash bottles can also be filled and stored with a variety of solvents. Methanol, isopropyl alcohol, ethanol, and acetone are common solvents. A wash bottle is constructed of plastic and has a screw-top cap. The plastic is intended to be flexible so that the bottle may be squeezed by hand to produce pressure that pushes the liquid in the bottle to flow through the plastic tube and out, either as a single drop or a narrow stream, onto the surface being cleaned.
Wash bottles are opaque, translucent, or transparent, with pre-printed measures. Wash bottles are useful for disinfecting a lab worktop with bleach, rinsing and washing reusable glass and plastic equipment, cleaning electrodes, working with harsh chemicals, and bringing reagents to volume.

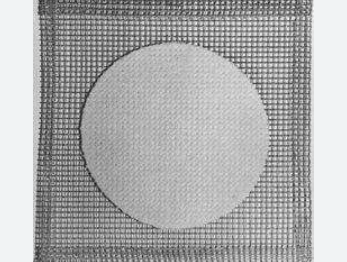
Wire Gauze
A wire gauze is a thin metal sheet with net-like or wire mesh patterns. Wire gauze is put between the Bunsen burner and the glassware on the support ring attached to the retort stand to support the beakers, flasks, or other glassware during heating.A wire gauze is formed out of a square wire mesh composed of steel, stainless steel, or another refractory alloy (Nichrome, for example), with a circular ceramic or asbestos cloth sandwiched in the middle. In order to support the beakers or other glassware or flasks during heating, the wire gauze is put on a tripod or support ring attached to the retort stand between the Bunsen burner and the beakers.
References
- https://www.labkafe.com/blog/a-list-of-chemistry-laboratory-apparatus-and-their-uses#:~:text=Ring%20stands%2C%20rings%2C%20and%20clamps,even%20distribution%20of%20the%20heat.
- https://www.vedantu.com/evs/uses-of-laboratory-apparatus
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Hope_College/General_Chemistry_Labs/Lab_Equipment
- https://studiousguy.com/list-of-chemistry-laboratory-apparatus-and-their-uses/
- https://microbeonline.com/equipment-required-for-chemistry-laboratory/
- https://scienceinfo.com/chemistry-lab-glassware/

