Interesting Science Videos
Expression for the Concentration of Solution
Normality: The normality of the solution is defined as the number of gram equivalent of solute dissolved in 1 litre of the solution.
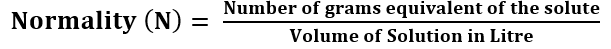
Molarity: The molarity of the solution is defined as the number of moles of solute per litre of the solution.
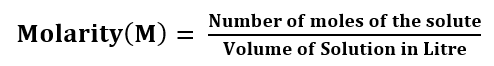
Formality: The formality of the solution is defined as the number of formula weight of the solute dissolved in 1 litre of the solution. It is used to express the concentration of ionic substances.
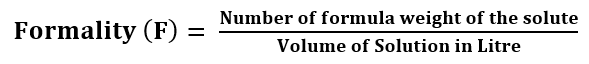
Molality: It is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved in 1 Kg of the solvent.
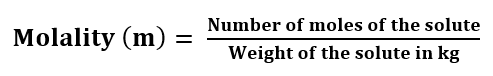
Mole Fraction: The ration of the number of moles of the component to the total number of the moles of all components (solute and solvent) present in the solution.
Let us consider a solution containing n moles of solute and N moles of solvent
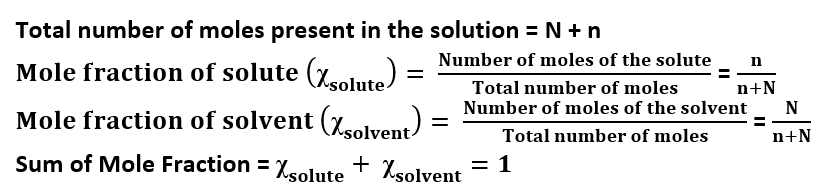
Gram per litre: It is defined as the amount of solute in gram present in 1 litre of the solution.
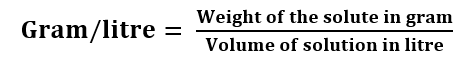
Percentage by Weight (% as w/w): It is defined as the weight of the solute in gram present in 100 gm of the solution.

Percentage by Volume (% as w/v): It is defined as the weight of solute in gram present per 100 ml of the solution.
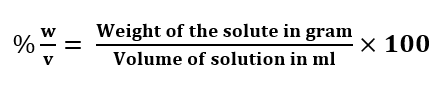
Formulas of Lowering of Vapour Pressure
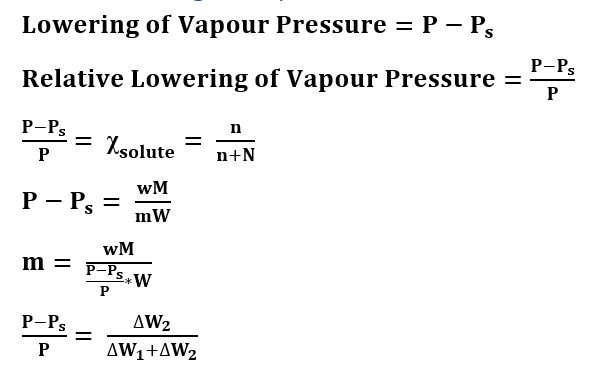
P = Vapour Pressure of Pure Liquid
Ps = Vapour Pressure of the solution
M = Molecular Weight of solvent
m = Molecular Weight of solute
w = weight of solute
W = weight of solvent
Formulas of Elevation of Boiling Point
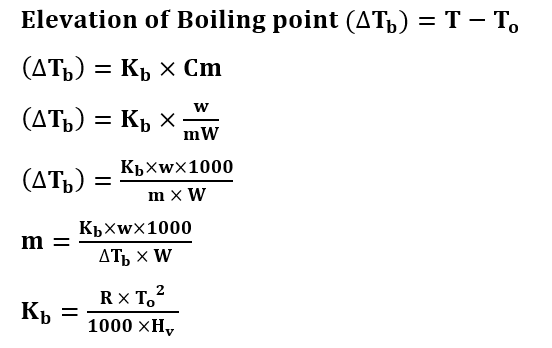
T = Boiling Point of Solution
To = Boiling Point of Solvent
Kb = Molal Elevation constant
Cm = Molality of the solute
Hv = Latent heat of vaporization
Formulas of Depression of Freezing Point

T = freezing point of the solution
To = Freezing point of the solvent
Kf = molal depression constant
Hf = Latent Heat of fusion
Formulas for Osmotic Pressure
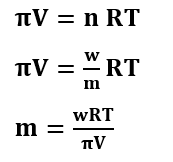
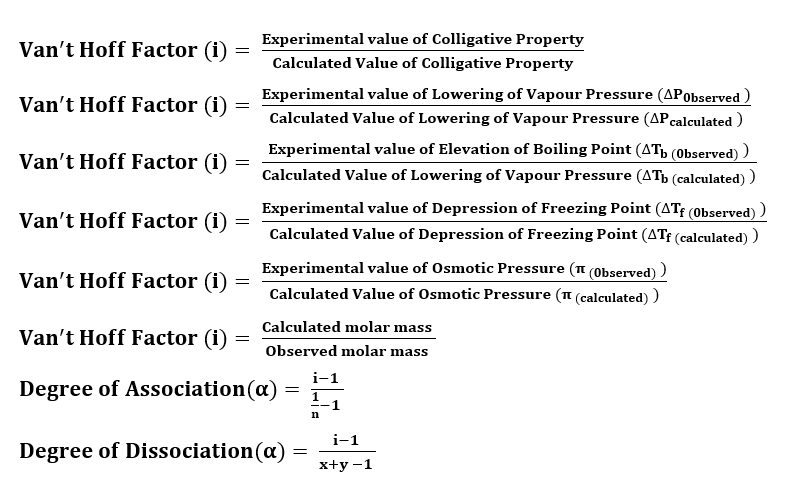
Formulas for Van’t Hoff Factor