Interesting Science Videos
Oxidation Definition
Oxidation is a chemical process involving the loss of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion, which increases the oxidation state of the chemical species.
- The historical definition of oxidation was based on the addition of oxygen to a compound as oxygen gas was the first known oxidizing agent.
- This definition aligns with the concept of electron loss and an increase in the oxidation state; however, the definition was later modified to include other types of chemical reactions.
- Oxidation reactions are often associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, but it has been observed that oxygen is not necessarily required in such reactions as other molecules can perform the same function.
- Oxidation reactions always occur with reduction reactions as the loss of electrons from a chemical species means the gain of electrons in another chemical species. Such reactions are termed redox reactions.
- The chemical species undergoing an oxidation reaction is said to be oxidized as it undergoes an increase in the oxidation state.
- Chemical substances that oxidize other substances are called oxidizing agents or oxidants. Oxidants remove electrons from other species while themselves being reduced.
- Oxidizing agents accept electrons, and thus, these are also known as electron acceptors.
Reduction Definition
Reduction is a chemical process involving the gain of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion, which decreases the oxidation state of the chemical species.
- The historical definition of reduction, like oxidation, was based on the removal of an oxygen atom from a molecule.
- The definition has been modified since to include reaction, which causes a decrease in the oxidation state of the chemical species.
- Besides, reduction also results from the addition of hydrogen atoms, which causes an increase in the negative charge of the species.
- Reduction occurs along with oxidation as a part of redox reactions as the loss of electrons during oxidation results in a gain of electrons to other species, resulting in reduction.
- Chemical substances that reduce other species are called reducing agents or reductants. Reductants donate electrons from chemical species while themselves being oxidized.
- The chemical species undergoing a reduction reaction is said to be reduced as it undergoes a decrease in the oxidation state.
- Reducing agents donate electrons and, thus, are also known as electron donors.
8 Key Differences (Oxidation vs Reduction)
| Characteristics | Oxidation | Reduction |
| Definition | Oxidation is a chemical process involving the loss of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion, which increases the oxidation state of the chemical species. | Reduction is a chemical process involving the gain of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion, which decreases the oxidation state of the chemical species. |
| Electron change | Oxidation involves the loss of electrons. | Reduction involves the gain of electrons. |
| Oxygen atom | Oxidation results from the addition of an oxygen atom. | Reduction results from the removal of oxygen atoms. |
| Hydrogen atom | Oxidation results from the removal of a hydrogen atom. | Reduction results from the addition of hydrogen atoms. |
| Oxidation number | The oxidation state of the chemical species increases after oxidation. | The oxidation state of the chemical species decreases after reduction. |
| Charge on the species | Oxidation results in an increase in the positive charge of the chemical species. | Reduction results in an increase in the negative charge of the chemical species. |
| Agents | Oxidation is caused by oxidizing agents or oxidants. | Reduction is caused by reducing agents or reductants. |
| Examples | An example of oxidation is the oxidation of glucose during internal respiration. | An example of reduction is the reduction of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. |
Examples of Oxidation
Cellular Respiration
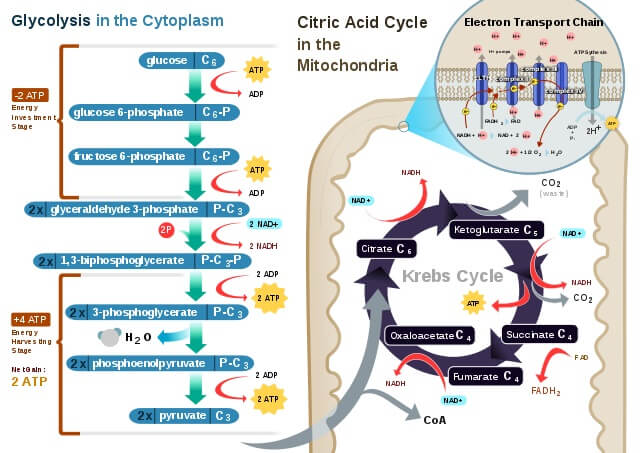
Image Source: RegisFrey.
- Cellular respiration involves the oxidation of glucose into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen.
- Since all oxidation reactions also involve a reduction reaction, oxygen is reduced to water.
- The oxidizing agent in the process is the oxygen molecule which itself gets reduced.
- The oxidation of carbon atoms changes from 0 to 4 as a result of the oxidation process, whereas the oxidation state of oxygen changes from 0 to -2.
- Cellular respiration falls under the classical definition of oxidation as oxygen acts as the oxidizing agent.
Examples of Reduction
Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is the reduction of carbon dioxide into a carbohydrate molecule in the presence of sunlight.
- The carbon dioxide molecule gains electrons during the process, which makes the molecule less positive and more negative.
- The overall charge of the molecule is reduced as a result of the added electrons, which are generated by the energy from photons.
References and Sources
- Gautum SD, Pant M and Adhikari NR (2016). Comprehensive Chemistry, Part 2. Sixth Edition. Heritage Publishers and Distributors Pvt. Ltd
- https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-oxidation-in-chemistry-605456 – 29%
- https://chem301r6.athabascau.ca/unit02.htm – 4%
- https://www.britannica.com/science/oxidation – 2%
- https://quizlet.com/289641912/chem-redox-reactions-dynamic-module-flash-cards/ – 2%
- https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-oxidation-and-vs-reduction/
