Molecules Definition
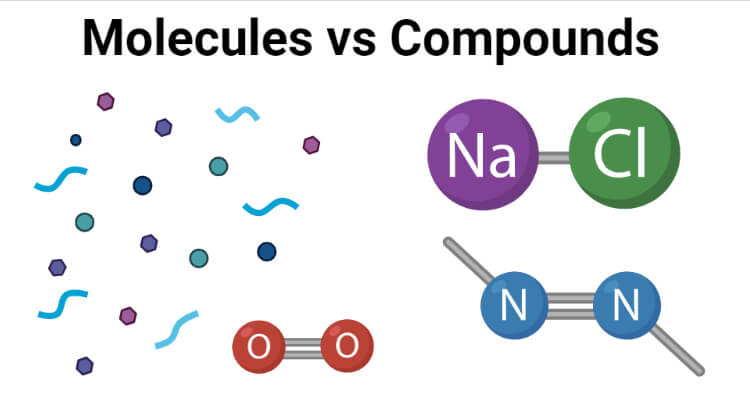
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms of the same or different atoms that represent the smallest identifiable unit of a substance that has the composition and chemical properties of the substance.
Molecules are individual units of a pure substance or a compound that interact with each other to provide structure and other properties to the compound.
- These are formed when the atoms come close enough so that their electron cloud can interact with each other as well as the nuclei.
- Molecules can either be homonuclear or heteronuclear. Homonuclear molecules are composed of atoms of the same element, whereas heteronuclear molecules have atoms of different elements.
- Molecules can further be divided into different groups depending on the type of bond present between the atoms. The bonds involved in molecules can be covalent or ionic bonds.
- In a particular molecule, the ratio of the number of atoms present remains fixed depending on the electronic configuration of the atoms.
- Molecules can also be diatomic (two atoms) or polyatomic (more than two atoms), depending on the elements.
- The structure of molecules is defined by the arrangement of the bonds, which are mostly directional as atoms tend to acquire positions that maximize the bond strength.
- The number of molecules in a mole of a substance remains the same in all substances and is known as Avogadro’s number (6.022×1023).
- The mass of a molecule can be determined by calculating the molecular weight, which is the sum of the atomic weight of the atoms present in the molecule.
- Molecules of a substance are represented by molecular formulas that utilize symbols, numbers, and other special characters.
- Molecules are smaller units of compounds where they interact with each other via van der Waal’s force of attraction.
- Some examples of molecules are O2, N2, H2, NH3, CO2, etc.
Compounds Definition
Compounds are chemical substances that are composed of molecules containing two or more atoms of different elements that are linked together by chemical linkages.
- Compounds are of different types, each defined by the type of elements and chemical bonds present. Compounds can be covalent, ionic, or metallic in the presence of covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds.
- The properties of the compound are determined by the number of atoms and the type of bonding present between the atoms.
- Some compounds can also be formed by chemical reactions between two different compounds where the bonds in the original compounds are broken, and new bonds are formed.
- There are more than 3000 different compounds that have been registered for use throughout the world.
- Compounds, like molecules, have defined stoichiometric proportions of atoms which are the same in the compound irrespective of the source.
- Compounds are always heteronuclear as they contain atoms of different elements and are also considered impure substances. If the atoms of the same elements are bonded together, these are not considered compounds.
- Chemical compounds are represented by chemical formulas, also known as molecular formulas, that are composed of symbols, numbers, and symbols.
- Compounds tend to have rigid structures as the molecules are either arranged (in solids) or distributed (gases). Depending on the interaction between the molecules and their sizes, the structure and rigidity of compounds are determined.
- Compounds can be broken down into individual elements via chemical reactions resulting in the breaking of chemical bonds.
- These are also more stable as these have a physical form, unlike molecules which are comparatively less stable.
10 Key Differences (Molecules vs Compounds)
| Characteristics | Molecules | Compounds |
| Definition | A molecule is a group of two or more atoms of the same or different atoms that represent the smallest identifiable unit of a substance that has the composition and chemical properties of the substance. | Compounds are chemical substances that are composed of molecules containing two or more atoms of different elements that are linked together by chemical linkages. |
| Elements | Molecules can be composed of atoms of the same or different elements. | Compounds are composed of atoms of different elements. |
| Unit | Molecules are considered the smallest unit of compounds or other pure substances. | Compounds are composed of molecules. |
| Category | Molecules can be both homonuclear as well as heteronuclear. | Compounds are heteronuclear. |
| Bonding | Molecules have covalent and ionic bonds. | Compounds have ionic, covalent, or metallic bonds. |
| Nature | All molecules do not form compounds. | All compounds have molecules. |
| Structure | Molecules do not have defined shapes or rigid structures. | Compounds are actual matter with definite shapes and structures. |
| Visibility | Molecules cannot be observed with naked eyes as they tend to microscopic. | Compounds can be observed with naked eyes depending on their size. |
| Stability | Molecules are less stable than compounds, and the stability depends on the type of atoms and their bonding. | Compounds are much more stable than molecules as they have a physical form. |
| Examples | Some examples of molecules are O2, N2, H2, NH3, CO2, etc. | Some examples of compounds are magnesium chloride, sodium chloride, zinc sulfate, etc. |
Examples of Molecules
Ozone (O3)
- Ozone is an unusual type of oxygen molecule consisting of three oxygen atoms bonded to each other via covalent bonding.
- Ozone is also known as a trioxygen molecule as it is different from the regular two-atom oxygen molecule.
- It is called an allotrope of oxygen and is less stable than the diatomic oxygen molecules.
- Ozone is formed from diatomic oxygen in the presence of UV light and electrical discharges in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- It found throughout the atmosphere, but the highest concentration remains at the ozone layer of the stratosphere. Since it is relatively unstable, it readily breaks down to form dioxygen at the lower atmospheric levels.
- Ozone is an essential part of the atmosphere as it prevents the UV lights from entering the Earth’s surface.
- Ozone is a strong oxidant that is used in different industries for applications related to oxidation.
Examples of Compounds
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Sodium chloride, also known as table salt, is an ionic compound composed of sodium and chlorine atoms.
- The compound exists in a solid crystalline state where the molecules are arranged in crystal lattices. Each ion is surrounded by six oppositely charged ions to form a regular octahedron.
- Sodium chloride is naturally found in the sea, where small particles of sea salt either remain suspended or are extracted.
- The sodium and chlorine atoms are present in a 1:1 ratio and are linked together by a single ionic bond.
- Sodium chloride is an essential component of our diet as it determines the salt concentration in various bodily fluids.
References
- Gautum SD, Pant M and Adhikari NR (2016). Comprehensive Chemistry, Part 2. Sixth Edition. Heritage Publishers and Distributors Pvt. Ltd
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/difference-between-molecule-and-compound/
- https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/difference-between-molecule-and-compound
